
The growing global concern about climate change is driving the refrigeration industry to transition to low-GWP refrigerants. With its extremely low GWP value, A2L refrigerants can not only help companies achieve global goals in the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol, but also meet the requirements of regional regulations such as the American Innovation and Manufacturing Act, Canada's Ozone Depleting Substances and Halogenated Hydrocarbons Regulation (ODSHAR), and the EU Green Deal. This has led to the widespread use and promotion of A2L refrigerants around the world. Against this backdrop, A2L solutions: hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs) and their blends, such as R1234yf, R454B, and R455A - have emerged as emerging alternatives to help the world phase out traditional refrigerants. Take R1234yf as an example. Compared with the old refrigerant R-134a, its global warming potential is reduced by up to 99%, showing significant environmental advantages.
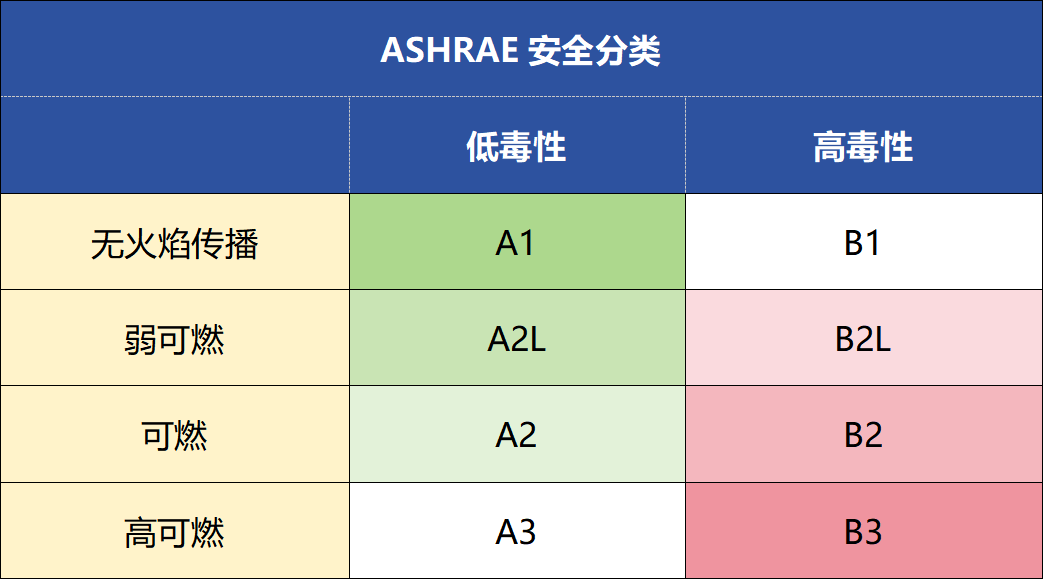
A2L refrigerant, with its weak flammability, low toxicity and significantly low global warming potential (GWP), is helping the world gradually move towards the transition to traditional refrigerants. Although A2L refrigerant is slightly flammable, it is generally handled properly and there will be no safety issues during use.
A2L refrigerant also has good thermodynamic properties and can meet the needs of various refrigeration equipment. Whether it is a household air conditioning system or a large commercial and industrial air conditioning system, A2L refrigerant can provide a stable cooling effect. At the same time, with the continuous advancement of technology, the performance of A2L refrigerant is continuously improving to better meet market demand.




